BIT: Bone Investigational Toolkit
BIT builds on the technology of both QCT Pro and CliniQCT. Choose to scan patients with a phantom for long-term precision, or analyze cases without a phantom for dual-use, retrospective, or prospective screening. Choose from investigational tools expanding measurement capabilities to include cortical thickness, moments of inertia, tissue composition, and more.
Choice of Calibration
Perform a monthly QA scan and choose on the fly whether you want to analyze a case with or without a phantom.
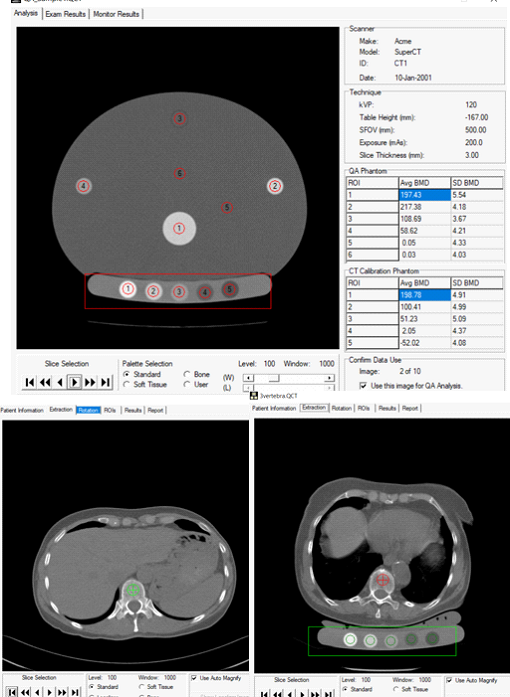
Research Tools—For Investigational Use Only
BIT is a collection of tools offering new measurement capabilities and utilities to support your research activities. BIT extends the measurement capabilities of the CTXA Hip Module to include reporting of various measurements of bone geometry not provided in a standard clinical hip analysis. Examples include cortical thickness, cross-sectional area and cross-sectional moment-of-inertia.
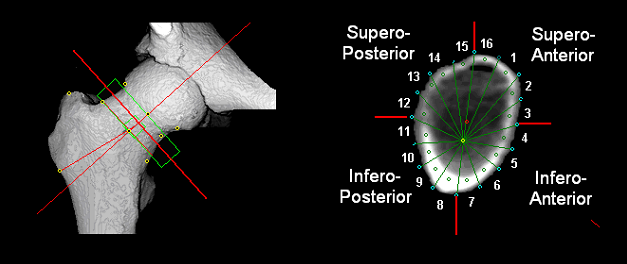
CT-BIT
CT-BIT is a version of the CTXA Hip module plus BIT that is intended for use at anatomical sites other than the proximal femur. With CT-BIT, measurements like those available from the CTXA Hip Module including BIT can be obtained at areas including the tibia, femur, radius and most other anatomical locations where the local bone cross-sections being characterized with CT-BIT have an approximate cylindrical symmetry.
Volumetric pQCT
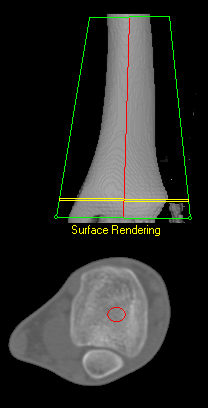
Until recently, pQCT has usually been performed on a dedicated machine, but there are significant advantages to performing pQCT bone density assessment on a clinical Whole Body Scanner using BIT:
- The cost of adding a QCT system to a standard CT scanner is considerably less than the cost of a dedicated pQCT machine;
- Patient motion artifacts are reduced with scan times of a few seconds instead of the 90 seconds per slice using a dedicated pQCT machine;
- Accurate matching of sections of bone during growth are feasible with a volume compared with scanning a few slices using a dedicated machine.
Tissue Composition Module (TCM)
TCM extends the capabilities of BIT to the assessment of fat and lean tissue quantity at peripheral sites, and measurement of abdominal fat, including the estimates of fat in separate visceral and subcutaneous tissue compartments. Additional information regarding the tissue composition module is available here.
The Bone Investigational Toolkit Includes:
Data Export
BIT analysis results are stored in the standard QCT Pro™ database. The database contents can be exported as delimited text files that can be imported into applications such as SPSS® or Excel® or other applications for further data processing and statistical analysis. Additionally, 2D projection images, cross-sectional images and reformatted volumetric data sets can be exported in DICOM format for use in your own or third-party applications.
Contact us for a quote or more information, or learn how Mindways supports Research.

